BIC Process Design
Understand & Transform
Supercharge your business operations with the most intuitive AI-powered BPM software.
It seems that you come from a German speaking country. Here you can change the language
EnglishAre you - like many other companies - facing the problem of tasks and responsibilities not being clearly defined? Then you are probably familiar with the following issues: lack of communication between departments in cross-functional tasks, unclearly defined accountabilities for business processes, or tasks that are carried out slowly and error-prone. With the help of the RACI Matrix, you can effectively address these problems and ensure clarity in assigning responsibilities and tasks by creating a systematic framework. We will show you in four steps how to successfully set up a RACI diagram for your company.

The RACI Matrix is a commonly used tool in project management and organizational development, providing a clear overview of responsibilities and tasks within a project. It is also utilized in process management to define roles and responsibilities within processes. It assists the involved roles in clarifying process tasks and assigning tasks to relevant team members. The RACI Matrix provides answers to the following questions:
RACI is an acronym that stands for Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed. In the RACI Matrix, these four attributes serve as a link between the involved roles and the assigned activities.
Responsible
A person with the "Responsible" attribute is directly responsible for carrying out a task. They ensure that the expected outcome is achieved. In some cases, this role may not perform the task (completely) themselves but rather initiates it and delegates it to other team members. In rare cases, this status may be assigned when someone has disciplinary responsibility for other team members. In such cases, task execution may be mandated by instruction.
Accountable
On the other hand, the "Accountable" person does not perform the tasks themselves but ensures that the results meet quality management expectations and requirements. Therefore, this person provides the necessary resources to achieve quality goals, reviews and approves activities, or releases processes upon completion.
Consulted
Roles with the "Consulted" status review and sign off on the work before it is handed over. These individuals are consulted to provide their opinion or support before activities are implemented. They possess the expertise relevant to achieving a specific outcome or completing a task.
Informed
The "Informed" person is updated on the progress and completion of an activity. This can be done in two ways: either there is an obligation to inform (push model, where other team members must regularly inform the person about progress) or the person has the right to information (pull model, where the person actively seeks information from others). In some cases, this person may not be involved in any other aspect of the work result.
It is important to know that there is no universal validity regarding role designations. Therefore, all stakeholders should be familiar with the tasks, rights, and responsibilities of each role at the beginning of a project to ensure smooth communication and collaboration, minimize misunderstandings, and increase the efficiency of process work.
Let's assume there is an onboarding process for new colleagues. This leads to various sub-activities that can emerge from the onboarding process:
A successful onboarding process requires the collaboration of multiple individuals and departments to ensure the seamless integration of new employees.
The involved individuals/departments include:
Each person involved in the process is assigned a RACI role within each task. For the task "Development of an onboarding plan", the role assignments could look like this:
Responsible: HR department
The HR staff member is responsible for designing and implementing the onboarding plan. This person creates the onboarding plan, develops the necessary steps and activities in consultation with the team leader, and ensures that all essential resources are provided.
Accountable: Team leader
The team leader is accountable for the success of the onboarding process, sets the expectations and goals for the new employee, and regularly reviews the progress during the onboarding period.
Consulted: IT support
The IT staff member provides the required IT resources (such as setting up user accounts, email addresses, access rights, etc.). They ensure that all technical aspects required for the new employee's tasks are taken into account.

Informed: Department manager
The department manager is informed about the progress of the onboarding process to coordinate tasks within the team and redistribute them if necessary, with the goal of reducing workload or improving team efficiency. They ensure the smooth integration of the new employee into the team.
Consulted: New employee
The new employee actively participates in the onboarding process. They introduce themselves to the team, learn about the company's products or services, and receive training relevant to their daily work. Without their involvement, these tasks/activities cannot be carried out.
There may be situations or processes where a person's role changes constantly: The responsible person in one task may become the informed role in the next task and then the accountable person in the following task. To clearly distinguish responsibility areas within a task, it is helpful to use the RACI diagram to track the tasks.

Clarity in assigning responsibilities

Avoidance of responsibility gaps

Transparency and traceability

Improved collaboration

Conflict prevention and resolution

Increased motivation

After assigning a name, the selected BPMN diagram will automatically open. Place a pool from the symbol palette into the editor using drag & drop. Next, create lanes to represent the individuals involved in the process. Within each lane, model the tasks/activities of each role and add artifacts (data objects, norms, applications, risks, etc.).

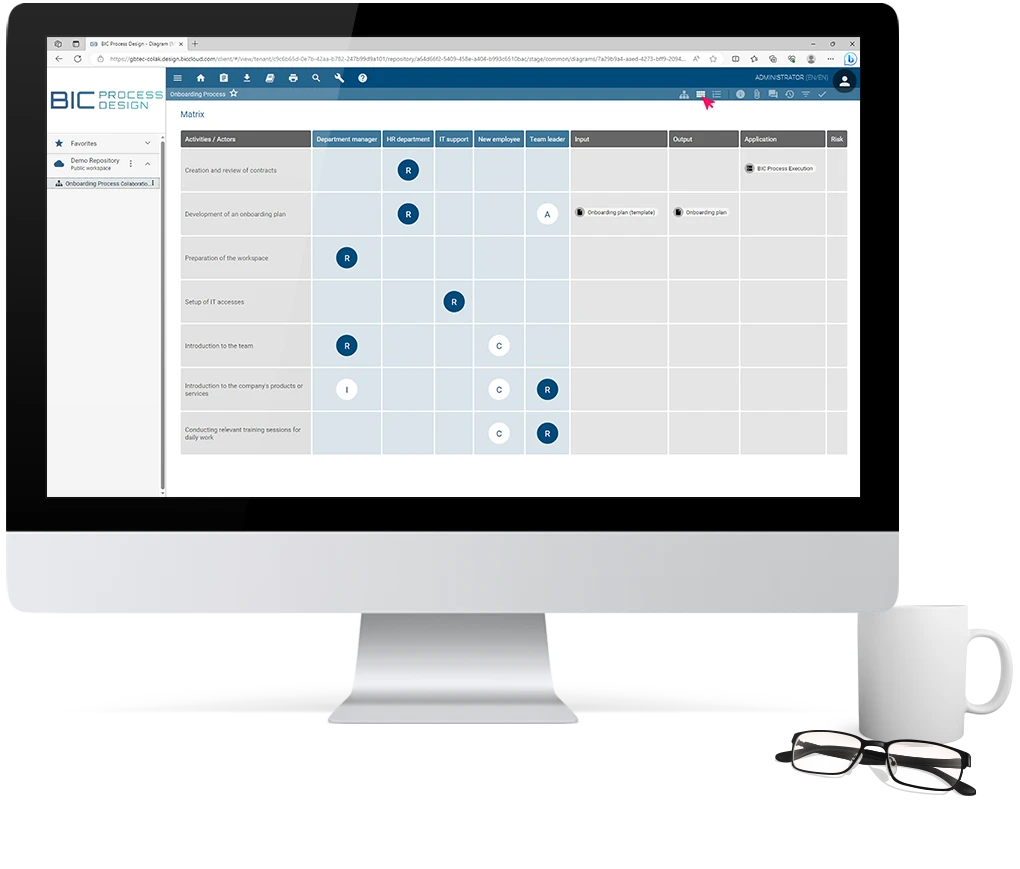
BIC Process Design automatically generates a RACI view based on the modeled process, without any additional steps. Select the matrix icon in the menu bar, and you will immediately access the automatically generated matrix view.
Depending on the process flow, all activities/tasks are listed vertically along the Y-axis. The roles involved in these tasks are displayed in columns side by side in alphabetical order. The type of connection (R, A, C, I) between the activity and the person is represented in the corresponding cells.
Click on the Process Execution icon in the menu bar. Based on the process model, the activities, decisions, and related events will be listed in the form of an interactive checklist. The Process Execution view allows for a visual understanding of the process flow, making it easy for employees without BPMN knowledge to grasp the workflow quickly and effortlessly. Additionally, this approach allows for an easy "walkthrough" of the process, examining potential areas for optimization before automating it in BIC Process Execution.


After releasing the "Onboarding Process" for automation in BIC Process Design, it will be directly displayed in BIC Process Execution. Now, click on the plus sign next to "Onboarding Process" and create a new case.
In BIC Process Execution, a form is created for each task when creating a case. This form serves as an information source and input screen to complete the respective tasks within the Onboarding Process. Once a case is created, every team member will be automatically notified when a new task is due. This ensures transparent communication within the team, managed and automated through the tool. Email chaos, missed deadlines, and the cumbersome input of tasks into inflexible third-party systems are now things of the past.


Associate Manager BPM Services
Jan helps clients successfully execute their process management projects and achieve sustainable improvements. As an Associate Manager in BPM Services, he combines in-depth expertise with a hands-on approach to develop tailored solutions for his clients' unique challenges. Together with his team, he ensures that companies enhance their efficiency and achieve long-lasting results.
We have the information you need to unleash your full process potential. Take a look at our resources and start improving your business performance today.